Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare, congenital disorder that can cause a distinctive “tower-shaped” head. There is no cure for Pfeiffer syndrome, but treatments are available to improve the symptoms. In this article, we will take a closer look at what Pfeiffer syndrome is, how it is diagnosed, and what treatments are available. We will also explore what it is like to live with Pfeiffer syndrome. After reading this article, you will be armed with the knowledge you need to better understand this condition.
Concise
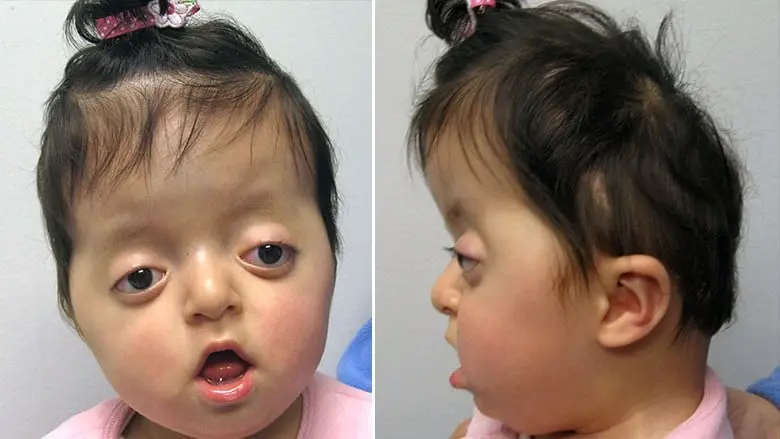
Pfeiffer Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the skull and face. It is characterized by cranial suture synostosis, which results in the premature fusion of the skull bones. This can cause a number of abnormalities in the skull and face, including a bulging forehead, underdeveloped midface, and an abnormal shape of the head.
There are three types of Pfeiffer Syndrome, classified based on the severity of the symptoms, which can range from minor to severe. The condition is caused by genetic mutation, and it can be inherited or occur spontaneously. With proper medical management and therapy, many individuals with Pfeiffer Syndrome can live a normal lifespan. Family members play an important role in the patient’s care and well-being and should take precautions and responsibilities accordingly.
Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare, congenital disorder that affects the development of the skull, face, and hands. It is characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones in the skull, which can lead to a distinctive “tower-shaped” head. There is no cure for Pfeiffer syndrome, but treatments are available to improve the symptoms.
Pfeiffer syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FGFR2 gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein that is involved in the development and maintenance of many tissues and organs. The FGFR2 protein is involved in signaling during embryonic development. Mutations in the FGFR2 gene can cause Pfeiffer syndrome type 1, type 2, or type 3.
Pfeiffer Syndrome Diagnosis
Pfeiffer syndrome is diagnosed based on clinical features and radiographic findings. A CT scan or MRI of the head can be helpful in making the diagnosis. The diagnosis can be confirmed with genetic testing.
The clinical features of Pfeiffer syndrome can vary depending on the severity of the condition. In general, people with Pfeiffer syndrome have a distinctive “tower-shaped” head, due to premature fusion of certain bones in the skull. They may also have developmental delays, broad thumbs and first toes, and problems with the middle ear bones. In some cases, people with Pfeiffer syndrome may also have abnormalities of the bones in their fingers and an underdeveloped or absent thumb on one hand.
Radiographic findings that may be seen in people with Pfeiffer syndrome include cranial bossing (prominent forehead), shallow orbits (eye sockets), midface hypoplasia (underdeveloped middle part of the face), and cloverleaf skull deformity. ACT scan or MRI of the head can help to confirm the diagnosis.
The diagnosis of Pfeiffer syndrome can be confirmed with genetic testing. This test looks for mutations in the FGFR2 gene, which is known to cause Pfeiffer syndrome.
Pfeiffer Syndrome Treatment
There is no cure for Pfeiffer syndrome, but treatments can improve the quality of life for those affected. The most common symptom of Pfeiffer syndrome is hydrocephalus, which can be treated with a shunt. Other symptoms of the syndrome include craniosynostosis, developmental delays, and problems with the middle ear bones. These symptoms can be treated with surgery, physical therapy, and occupational therapy.
Living
Living with Pfeiffer syndrome can be difficult, as the disorder can cause a number of different symptoms that can affect many different areas of life. It is important for people with Pfeiffer syndrome to receive lifelong medical care from a team of specialists. There are also a number of support groups and resources available for people with Pfeiffer syndrome and their families.
The most common symptom of Pfeiffer syndrome is hydrocephalus, which occurs when there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Hydrocephalus can be treated with a shunt, which is a device that drains the excess fluid from the brain and into another part of the body where it can be absorbed.
Craniosynostosis, another common symptom of Pfeiffer syndrome, occurs when the bones in the skull fuse prematurely. This can cause problems with brain development and lead to a distinctive “tower-shaped” head. Craniosynostosis is treated with surgery to correct the deformity and allow for normal brain growth.
People with Pfeiffer syndrome may also experience developmental delays, problems with their middle ear bones, and abnormalities of the bones in their fingers. These symptoms can be treated with physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other interventions.
It is important for people with Pfeiffer syndrome to receive lifelong medical care from a team of specialists. This team may include a neurologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedic surgeon, plastic surgeon, and geneticist. These specialists will work together to monitor the symptoms of Pfeiffer syndrome and provide treatment as needed.
There are also a number of support groups and resources available for people with Pfeiffer syndrome and their families. These groups can provide emotional support and information about living with Pfeiffer syndrome.
Three Types of Pfeiffer Syndrome
Pfeiffer Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the skull and face. It is characterized by cranial suture synostosis, which results in the premature fusion of the skull bones. This can cause a number of abnormalities in the skull and face, including a bulging forehead, underdeveloped midface, and an abnormal shape of the head.
There are three types, classified based on the severity of the symptoms:
- Type 1: The most severe form, characterized by skull and facial abnormalities, including a very prominent forehead, shallow eye sockets, and a small jaw. This type of Pfeiffer Syndrome can also cause additional complications, such as hearing loss and difficulties with breathing and feeding.
- Type 2: Less severe form with fewer skull and facial abnormalities, as well as milder symptoms compared to type 1. Cranial suture synostosis is still present, but the skull and face may appear less affected.
- Type 3: The mildest form, with only minor skull and facial abnormalities, such as a slightly prominent forehead, but the cranial suture synostosis is less severe, and the symptoms are less pronounced.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Pfeiffer Syndrome
Pfeiffer Disease is a condition that affects the skull and face, causing a number of physical abnormalities. The symptoms of Pfeiffer Disease can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but may include:
- A bulging forehead
- Underdeveloped midface
- An abnormal shape of the head
- Cranial suture synostosis
- Hand and foot deformities
- Hearing loss
Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination and imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI. These tests can help identify the specific type and severity of Pfeiffer Disease, as well as any associated complications.
Life Expectancy For Individuals
The life expectancy for individuals with Pfeiffer Syndrome can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the presence of associated health issues. In general, individuals with milder forms of the condition have a normal life expectancy, while those with more severe forms may face additional complications that can affect their overall health and well-being.
With proper medical management and therapy, many individuals with Pfeiffer Syndrome can live a normal lifespan. Treatment may include surgery to correct skull and facial abnormalities, physical therapy to address hand and foot deformities, and hearing aids to address any hearing loss.
Causes of Pfeiffer Syndrome
Pfeiffer Syndrome is caused by a genetic mutation, which can be inherited or occur spontaneously. The condition is caused by mutations in one of the genes responsible for the development of the skull and face. The most common gene associated with Pfeiffer Syndrome is FGFR2.
Adults Living With Pfeiffer Syndrome: Managing the Condition in Later Life
Adults with Pfeiffer Syndrome may require ongoing medical management and therapy to address symptoms and complications. This may include surgery to correct skull and facial abnormalities, physical therapy to address hand and foot deformities, and hearing aids to address any hearing loss.
Support from family, healthcare professionals, and support groups can also be beneficial for individuals living with Pfeiffer Syndrome as an adult. These resources can provide emotional support, help with managing the condition, and connect individuals with others who are living with Pfeiffer Syndrome.
Important Points
Treatment options: In addition to the medical management and therapy mentioned previously, treatment for Pfeiffer Syndrome may also include medications to control pain and inflammation, as well as orthodontic treatment to address dental issues.
Impact on daily life: Pfeiffer Syndrome can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life, particularly in terms of physical and social functioning. Individuals with the condition may face challenges with activities of daily living, such as eating and speaking, as well as difficulties with social interactions and self-esteem.
Research and advancement: Pfeiffer Syndrome is a relatively rare condition, and research into the condition is ongoing. Advances in genetics and medical technology are helping to improve the diagnosis, treatment, and understanding of Pfeiffer Syndrome.
Coping and support: Living with a chronic condition like Pfeiffer Syndrome can be challenging, both for the individual and their loved ones. It’s important to have a support system in place, including access to counseling and support groups, to help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological impact of the condition.
Family With The Patient Of Pfeiffer Syndrome
The members of the family in which a patient with Pfeiffer Syndrome belongs play an important role in the patient’s care and well-being. It is essential for family members to be informed about the condition, its symptoms, and the treatment options available.
Precautions That Family Members Should Take Include:
- Understanding and being aware of the condition
- Learning about the treatment options and supporting the patient through the treatment process
- Encouraging the patient to follow the recommended treatment plan
- Being patient and understanding with the patient, as the condition can be physically and emotionally taxing
- Helping to ensure that the patient has access to the necessary medical and therapeutic resources
Responsibilities Of Family Members Include:
- Providing emotional support and encouragement to the patient
- Helping to coordinate the patient’s care, including scheduling appointments, managing medications, and providing transportation
- Helping to ensure that the patient has access to necessary resources, such as financial assistance or adaptive equipment
- Being a source of information and support for others, such as friends and extended family members
Conclusion
Pfeiffer Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the skull and face. Although it is a rare condition, it can have a significant impact on the individual’s life. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and support from family and healthcare professionals can help individuals with Pfeiffer Syndrome to manage the condition and lead a fulfilling life.
Last Worded From The Author To The Readers
As the author, my message to the readers is to raise awareness about Pfeiffer Syndrome and to highlight the importance of early diagnosis, proper treatment, and support from family and healthcare professionals. I hope that this information has been helpful in understanding the condition and the impact it can have on the individuals and their family members. If you or someone you know is affected by Pfeiffer Syndrome, know that there are resources available to help manage the condition and lead a fulfilling life.
Also Read